It is possible to have a healthy diet without animal products and still get the recommended nutrients. Before you switch to a vegan lifestyle, there are several things that you need to consider. You will need to replace certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin B12 from dairy products. These nutrients are almost exclusively found within animal products. These nutrients can easily be replaced by eating plant-based meals or by taking a nutritional supplement. A dietitian may be able to recommend suitable foods for replacing them.
They decrease the likelihood of 15 leading causes for death
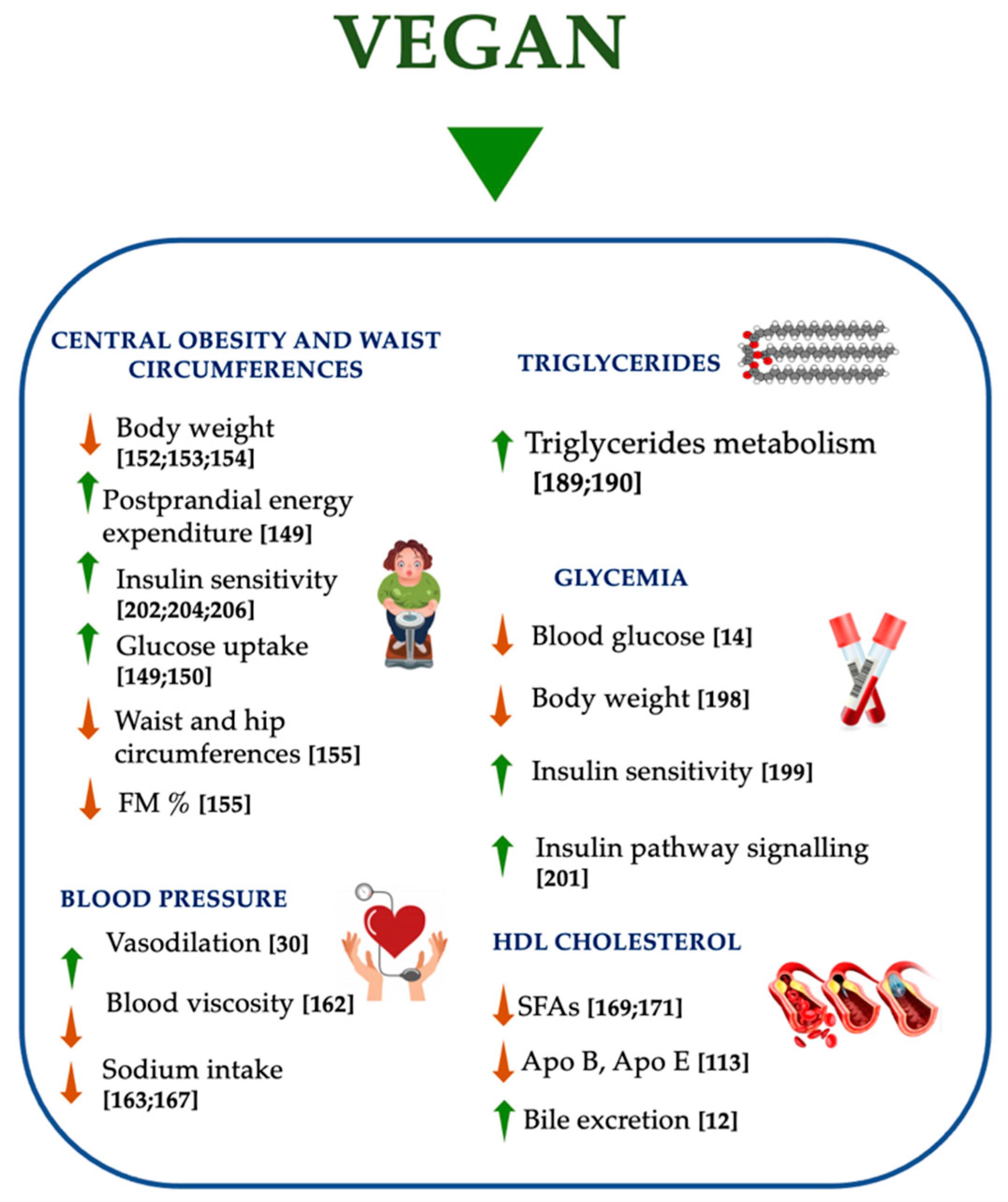
The world's largest killer, cardiovascular disease (CHD), kills 17.9 million people each year. Studies have shown that the risk of developing this disease is reduced when you eat vegetarian or vegan foods. CHD risks are reduced by around 20% in vegans and vegetarians, according to research. They had 10 less cases of CHD per 1000 people than meat-eaters. Many studies carried out by the Pan-European EPIC Cohort also revealed a reduction in CVD risk for meat eaters.
A new study in Nature Communications has shown that vegans are less likely to suffer from an ischemic stroke. The study included 15,000 people who had either a hemorrhagic stroke or a stroke caused by blockage of blood flow to the brain. These findings are encouraging, but further research is needed to confirm them.

They are environment friendly
Studies have shown that veganism can be more sustainable than eating animal products. Meat consumption is linked to higher emissions of greenhouse gases and deforestation. Land is wasted in the process of raising chickens, beef, and other animals for food. The livestock sector is destructive of our planet and depletes the soil's nutrients. This leads to habitat loss and deforestation.
It is no surprise that vegans have seen a 160 percent increase in their number over the past decade. When considering your meals, take the time to consider where your food comes from and how it was grown. Most meat comes from faraway places, but vegan food can be grown locally in many locations. Mangoes, for example, and pomegranates are both from India. There are also beans and lentils that have been grown in Canada or Brazil. Local farms are better for the environment that imports.
They are very easy to adapt to
You can make a simple switch to a plant-based diet by following these steps. You should carefully read the ingredient labels to ensure you only purchase products made with natural ingredients. Pay attention to ingredients such as carmine, red 4 and confectioner’s glazing, as they are all made from animal products. Some companies will even label their products as vegan at or near the beginning of the ingredient list.
It's important that you take things slow. Also, don't overcomplicate yourself by trying to make each meal a gourmet masterpiece. Moving to a vegan diet is easy if you go step by step, eating each meal one at a. Avoid feeling overwhelmed, and try to stick to one meal per day for a few weeks to get used to the new lifestyle.

They promote humane treatment and respect for animals
Being vegan is a great way to support humane treatment of animals. Refusing to purchase animal products will help reduce their demand. This in turn means that fewer animals are bred and killed in factories and farms. Every year, more than one billion animals in the UK are raised for food. These animals are often reared in factory farms and are usually killed when they reach a few months of age.
The philosophy of veganism is based on the belief that using animals for human purposes is cruel and unjust, and that a person of conscience should refrain from doing so. Vegans resolve to stop eating, using, and wearing animal products. Vegans also object to violence against animal species.
FAQ
Improve immunity with herbs and supplements?
It is possible to boost immune function by using herbs and natural remedies. Some common examples include garlic, ginger, oregano oil, echinacea, ginkgo biloba, and vitamin C.
These herbal remedies are not meant to replace medical treatment. Side effects include nausea, dizziness and stomach cramps.
How often do I need to exercise?
It is important to exercise for a healthy lifestyle. But, you don't need to spend a specific amount of time exercising. The key is finding something you enjoy and stick with it.
It is a good idea to exercise at least three times per week. Then, you should aim to do between 20 and 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity. Moderate intensity means you'll still be breathing hard after you've finished. This type is good for burning around 300 calories.
Walk for 10 minutes four days a semaine if you prefer walking. Walking is low in impact and easy for your joints.
You can also run for 15 minutes, three times per week. Running is a great way of burning calories and building muscle tone.
Begin slowly if your are new to exercising. You can start with only 5 minutes per week of cardio. Gradually increase the duration until you reach your goal.
How do I determine what's good?
Listen to your body. Your body knows what you need when it comes time to eat, exercise, and get enough rest. To be healthy, you must pay attention and not push yourself too hard. Take care of yourself and listen to your body.
Statistics
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- According to the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, a balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy and whole grains is needed for optimal energy. (mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
- nutrients.[17]X Research sourceWhole grains to try include: 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, brown rice, whole grain oats, farro, millet, quinoa, and barley. (wikihow.com)
- Extra virgin olive oil may benefit heart health, as people who consume it have a lower risk for dying from heart attacks and strokes according to some evidence (57Trusted Source (healthline.com)
External Links
How To
What does the word "vitamin" mean?
Vitamins are organic substances found naturally in food. Vitamins help us absorb nutrients from foods we eat. Vitamins cannot come from the body so food must provide them.
There are two types of vitamins: water soluble and fat soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve quickly in water. Some examples include vitamin C,B1 and B2 vitamins (thiamine), B2 and riboflavin, B3 and niacin, B6 vitamins (pyridoxine), B6 vitamins (niacin), folic acids, biotin, pantothenic acids, and Choline. Fat soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and fatty tissue. Examples include vitamin D, E, K, A, and beta carotene.
Vitamins are classified according to their biological activity. There are eight main groups of vitamins.
-
A – Essential for normal growth, and the maintenance of good health.
-
C - vital for nerve function and energy generation
-
D - essential for healthy teeth and bones.
-
E - Required for good vision, reproduction.
-
K - required for healthy muscles and nerves.
-
P – vital for building strong bones.
-
Q - aids digestion and absorption of iron.
-
R - Required for red blood cell production
The recommended daily allowance (RDA), for vitamins, varies based on gender, age, and physical condition. RDA values are set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
For adults aged 19 or older, the RDA of vitamin A is 400mg per day. For fetal development, pregnant women require 600 micrograms per daily. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Babies under one-year old need 700 micrograms per daily. Between 9 and 12 month, however, this drops to 500 mg per day.
Children ages 1-18years who are obese need 800 micrograms per day while those who are overweight need 1000 micrograms per day and children who are underweight need 1200 micrograms per day to meet their nutritional needs.
Children 4-8 years old with anemia will need 2200 mg of vitamin D daily.
2000 micrograms are required daily for good health in adults over 50. Mothers who are pregnant, nursing, or have a high nutrient need will require 3000 micrograms a day.
1500 micrograms is the recommended daily intake for adults aged 70+, as they lose 10% of their muscle every ten years.
Women who are pregnant or lactating need more than the RDA. Pregnant mothers need 4000 micrograms per daily during pregnancy and 2500 after giving birth. Breastfeeding mothers require 5000 micrograms daily when breast milk production is occurring.